Top News

Taller delitos ambientales y acceso a la justicia
BIOS Argentina-Nodo Tandil
El día 9 de septiembre se llevó a cabo la presentación de la conferencia del Fiscal Federal Antonio Gustavo Gómez en la Asociación de Abogados de Tandil y en la Asociación de Magistrados y funcionarios de Tandil.
La actividad también se enmarca en una serie que viene brindando el Fiscal Federal Gustavo Gómez en diferentes localidades de la región, al inicio propuestos y promovidos desde el Nodo Tandil de BIOS Argentina, con la activa participación de varias instituciones, organizaciones y colectivos socioambientales. Los cuales se han organizado para difundir, promover y realizar los talleres y conferencias sobre Delitos Ambientales y Acceso a la Justicia, propuestas por el Fiscal Federal.
El lunes 5 de septiembre también se realizó dicho taller a las 6 de la tarde en Tandil. Organizaron: Asamblea por un Tandil sin Trigo Transgénico ni Agrotóxicos; Centro Cultural y Radio La Compañía; Bios Argentina Nodo Tandil. En el Centro Cultural y Radio La Compañía. Se transmitió en forma virtual gracias al apoyo de IPEN (Red Internacional de Eliminación de Contaminantes), que brindó tanto su plataforma Zoom como el equipo técnico para poder hacerlo.
Si desea ver la presentación completa la puede descargar en el siguiente link.
More News
Upcoming Events
- International Lead Poisoning Prevention Week, 23–29 October 2022
Check the IPEN Lead Paint page for updates in early October - Plastics Treaty INC 1, 28 November – 2 December 2022 (a multi-stakeholder forum will be organized on 26 November)
Location: Punta del Este, Maldonado, Uruguay
Check IPEN’s Plastics Treaty page for Quick Views and other updates in November
Recent Reports
Argentina: Promoting the agroecological paradigm on the way to eliminating highly hazardous pesticides
Brazil: Território Sustentável
Chile: Country Situation Report on highly hazardous pesticides
Colombia: Mercury Trade and Supply in ASGM in Colombia
Costa Rica: El herbicida glifosato y sus alternativas (The herbicide Glyphosate and its alternatives)
Cuba: Los Plaguicidas Altamente Peligrosos en Cuba (Alternatives to highly hazardous pesticides in Cuba)
Jamaica: COVID-19 and Chemical Usage
Jamaica: Highly Hazardous Pesticides in Jamaica
Mexico: Prohibition of single-use plastics and Roll Back of Morelos Waste Law
Mexico: Asbestos in Mineral Talc and Healthier Alternatives
Uruguay: ¿Cuál es el problema con el talco y cómo se relaciona con el asbesto? (What is the problem with talc and how is it related to asbestos?)
Newest IPEN Reports
Hazardous Chemicals in Plastic Products
Both the environment in Africa and the Arabic region and the human health of Africans and people from Arabic countries suffer from toxic chemicals and imported wastes, including illegal wastes, more than in developed countries.
This study shows that toxic chemicals are present in toys, kitchen utensils, and other consumer products purchased from African and Arabic region markets in Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Egypt, Ethiopia, Gabon, Jordan, Kenya, Morocco, Syria, Tanzania, and Tunisia.
Plastic Waste Fuels
IPEN studies show how policy is driving massive investment in plastic waste-to-fuel processing, and that exports are threatening waste management in ASEAN countries and undermining the Basel Convention and climate change commitments.
Plastic Poisons the Circular Economy
IPEN published a number of studies showing significant obstacles for countries seeking to implement safe plastic circular economies. The studies reveal that countries are unable to handle large volumes of diverse plastics waste streams safely, and the reality that, without regulations requiring plastic ingredients to be labeled, countries are blindly allowing known toxic chemicals onto their markets in plastic products.
Plastic pellets found on beaches all over the world contain toxic chemicals
Preproduction plastics as pellets, or "nurdles", can carry many different chemicals, both those added to the plastics and pollutants that attach (sorb) to them in the environment. Often lost during production, transportation, and storage, pellets have been found on beaches all over the world since the 1970s. This study of plastic pellets gathered from beaches in 23 different countries contained many chemicals of concern, some in very high concentrations.
Widespread chemical contamination of recycled plastic pellets globally
Because almost all plastics contain toxic chemicals, recycling processes can perserve and can even generate toxic chemicals, such as dioxins. In this study, pellets made from recycled HDPE, intended for use in new products, were purchased from 24 recyclers in 23 countries and analyzed for 18 substances. The large number of toxic chemicals in many of the samples highlights the need to rethink recycling to ensure it does not perpetuate harms..
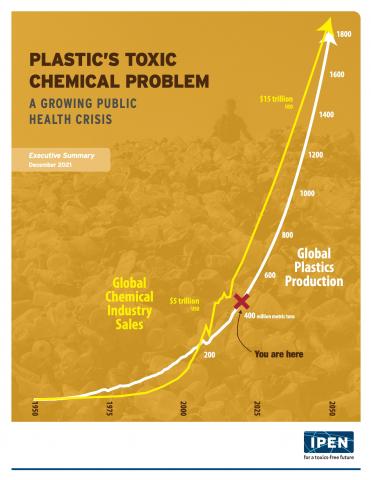
Plastic’s Toxic Chemical Problem: A Growing public health crisis
This summary of our two plastic pellets reports encapsulate the broad issues related to toxic chemicals in plastics and the concerns with recycling processes that can perserve or generate toxic chemicals.
Plastic Waste Management Hazards
Plastic waste has become an unprecedented pollution issue, blanketing our planet in the petrochemical remnants of plastic production. This report examines current and emerging methods by which plastic waste is managed globally and questions whether any of them present a solution to the rapidly accelerating generation of plastic waste. In short, they don't and the only long-term answer is to produce less plastic.
Regional Coordinator
Red de Accion en Plaguicidas y sus Alternativas para America Latina (RAPAM) / Centro de Analisis y Accion en Toxicos y sus Alternativas (CAATA)
Based in Mexico
RAPAM / CAATA has the mission to promote the progressive phase-out of hazardous chemicals that threaten human health and the environment, and to change public policy to support alternatives including agroecological agriculture, clean production and exercising rights for a healthy and toxics-free environment for the present and future generations.
Get our Newsletter
Video Highlight